Disinfection Technologies
Surface Disinfection / Decontamination
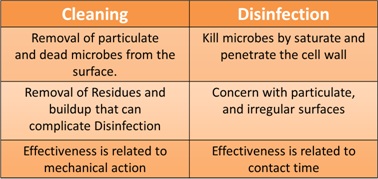
It’s important to note that cleaning a surface, such as removing dirt and particles, is not the same thing as disinfecting a surface that kills viruses and bacteria. Cleaning is still the key to achieve successful disinfection!
There are many products you can use to superficially clean hard surfaces However, those products have NOT been scientifically proven to effectively disinfect a surface from contaminants such as the coronavirus, influenza, norovirus, etc.
Types of Antimicrobial Agents
Antimicrobial agents are substances or mixtures of substances used to destroy or suppress the growth of harmful microorganisms whether bacteria, viruses, or fungi on inanimate objects such as walls, floors, ceilings, and other surfaces. Antimicrobial products may be categorized as follows;
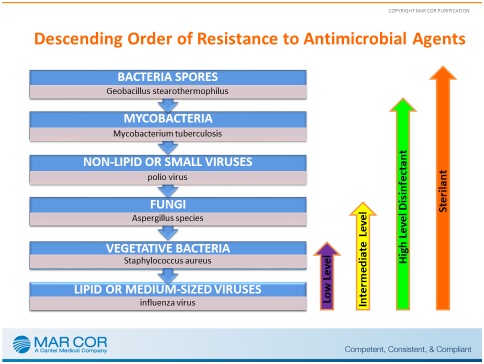
- Sterilisers (Sporicides): Used to destroy or eliminate all forms of microbial life including fungi, viruses, all forms of bacteria and their spores.
- Type of sterilisers include:
- Steam under pressure (autoclaving)
- Low temperature gas (ethylene oxide)
- High energy radiation (Gamma rays)
- Liquid chemical sterilants (such as Minncare, Actril)
- Type of sterilisers include:
- Disinfectants: Used on hard inanimate surfaces and objects to destroy or irreversibly inactive infectious fungi and bacteria but not necessarily their spores.
- Types of Disinfectants include:
- High level disinfectants:Kill all viruses and vegetative cells, but they may not kill endospores reliably.(E.g. Hydrogen Peroxide, Formaldehyde).
- Intermediate level disinfectants: Destroy all vegetative cells including Mycobacteria, fungi, and most, but not all viruses. They cannot kill endospores. (E.g. Alcohols)
- Low level disinfectants: Destroy vegetative bacteria, except Mycobacteria, fungi and non-enveloped viruses. (E.g. Quaternary ammonium compound)
- Types of Disinfectants include:
- Sanitisers: Used to reduce, but not necessarily eliminate, microorganisms from the inanimate environment to levels considered safe as determined by public health codes or regulations.
- Type of Sanitisers:
- Food contact products: Dishes and cooking utensils, equipment and utensils found in food processing plants.
- Non-food contact products: Carpet sanitisers, air sanitisers, laundry additives, in-toilet bowl sanitisers.
- Antiseptics and Germicides: Used to prevent infection and decay by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms. Because these products are used in or on living humans, they are thus approved and regulated.
- Type of Sanitisers:
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance happens when microorganisms (such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites) change when they are exposed to antimicrobial drugs (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintics). Microorganisms that develop antimicrobial resistance are sometimes referred to as “superbugs”.